Welcome to WordPress. This is your first post. Edit or delete it, then start writing!
Blog
-
Unveiling the Fascinating World of Satellites: 15 Amazing Facts
Unveiling the Fascinating World of Satellites: 15 Amazing Facts
June 9, 2023 Category: Satellite Communications
Satellites have become an integral part of our modern world, facilitating communication, navigation, weather forecasting, and much more. Behind their capabilities in enabling global connectivity and unrivaled insights into the mysteries of space lie remarkable facts that will leave you amazed.
#1 Satellite Lifespan: A Decade of Service
Satellites typically have a working life of 10 to 15 years, during which they provide critical services like communication, weather monitoring, and more.
#2 Space Fuel Conservation: The Dance of Orbit
Once a satellites reaches its designated orbit, it can maintain its position without consuming fuel. However, lower satellites experience atmospheric drag over time, requiring occasional fuel boosts to remain in their position.
#3 Farewell, Low Satellites
Low satellites with altitudes below 1,000 km are intentionally de-orbited when they cease to function. They reenter the Earth’s atmosphere, burning up in the process.
#4 Geo Satellites: Celestial Illusionists
Geostationary Orbit (GEO) satellites orbit the equator at the same speed as the Earth’s rotation, making them appear stationary in the sky. They create the illusion of being fixed in one position.
#5 Leo Satellites: Speed Demons in the Sky
Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites orbit the Earth at a staggering speed of 28,000 km/h.
#6 he Mighty ISS: Humanity’s Orbital Oasis
The International Space Station (ISS) holds the distinction of being the largest satellite, measuring a whopping 109 meters in length.
Permanently inhabited by a crew of 6 individuals, the station serves as a remarkable feat of human engineering and international collaboration. Every 6 months, the crew members are rotated, ensuring a continuous human presence in space and fostering groundbreaking research across various fields.
The construction and maintenance of the ISS have come at a significant cost, with the total expenditure exceeding a staggering $150 billion, making it one of the most ambitious and expensive projects in human history.
 Figure 1: International Space Station (ISS)
Figure 1: International Space Station (ISS)#7 GPS: 27 Satellites Guiding Our Way
The Global Positioning System (GPS) relies on a network of 27 satellites to provide accurate positioning and navigation services across the globe.
Figure 2: GPS Satellite
#8 Sputnik 1: The Trailblazer
The first man-made satellite, Sputnik 1, was launched into orbit by the USSR in 1957. Sputnik 1 was a little larger than a football and took about 98 minutes to orbit the Earth. The word ‘Sputnik’ means fellow traveler.

Figure 3: Sputnik 1#9 Vanguard-1: The Timeless Wanderer
Vanguard-1 holds the title of the oldest man-made satellite still in orbit, having been launched in 1958. It continues to circle the Earth, even after all these years.
#10 Graveyard Orbit: Resting Place for GEO Satellites
GEO satellites which are situated at an altitude of 36,000 km maneuver into a “Graveyard Orbit” at the end of their lives. This ensures that they remain out of the way of operational satellites.

Figure 4: Graveyard Orbit
#11 The Resurrected Satellite: LES1’s Surprising Return
In a fascinating turn of events, LES1, a satellite abandoned in 1967, recently started transmitting again due to the decayed batteries unexpectedly shorting the solar energy straight to the electronics.
#12 Messages for the Future: Satellites as Time Capsules
Satellites orbiting Earth today are estimated to re-enter the atmosphere in approximately 8.4 million years, carrying messages from our present civilization to future generations.
Figure 5: Current Starlink satellites across the globe
#13 Unveiling the Cosmos: Satellites with Mighty Telescopes
Some satellites like the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) carry colossal telescopes to enable the observation of remote galaxies and exoplanets, offering glimpses billions of years into the past.
#14 Tom and Jerry: Satellites on a Gravity Mission
In 2002, 2 satellites nicknamed Tom and Jerry embarked on a groundbreaking mission to investigate Earth’s shifting water masses and map their effects on the planet’s gravity field. Through their data collection, Tom and Jerry contributed invaluable insights into the understanding of Earth’s hydrological cycle and its intricate relationship with gravity.
#15 Suitsat-1: An Unconventional Satellite Endeavor
In a unique and whimsical experiment, the Russian space agency launched Suitsat-1 in 2006. This extraordinary satellite was actually a discarded Russian Orlan spacesuit equipped with various electronics. Suitsat-1 ventured into space, broadcasting amateur radio signals and transmitting images from its onboard cameras. It floated freely, resembling a spacesuit on a spacewalk. Although Suitsat-1’s mission was short-lived and lasted for only a few weeks, it captured the imagination of space enthusiasts and served as a testament to the creativity and ingenuity within the realm of satellite technology.

Figure 6: Suitsat-1
From LEO satellites racing through the cosmos to the unconventional experiment of Suitsat-1, satellites continue to astound us with their capabilities and discoveries. However, the realm of satellites isn’t just limited to these awe-inspiring moments. It’s a dynamic industry that requires expertise and knowledge to navigate successfully. That’s where satellite communications training becomes crucial.
Stay Ahead of the Orbit: Supercharge Your Professional Growth with Telefocal Asia’s Satellite Training
At Telefocal Asia, we recognize the importance of equipping individuals with the necessary skills and expertise to excel in the field of satellite communications. Our comprehensive satellite communications training programs provide in-depth knowledge of satellite communications principles and applications, radio link planning and budgeting, and much more.
Whether you’re an aspiring professional looking to embark on a satellite communications career or an organization seeking to enhance your capabilities, our courses offer the knowledge and expertise you’ll need to navigate this exciting world of satellite communications
Together, let’s unlock the boundless possibilities that satellites offer and shape a future where connectivity knows no bounds.
Contact us today to find out how we can help you succeed.
References:
- NASA
- Satnow.com
- Cosmos Magazine
- Ttweathercenter.com
Follow us on LinkedIn to stay tuned to our weekly updates of the latest developments in the Telecom/IT industry and popular courses that we offer.
Share this on…
-
5G Types: Fast to Faster to Fastest
5G Types: Fast to Faster to Fastest
May 7, 2021 Category: 5G Technologies
5G can be implemented in multiple ways, three of which are most prominent and are being targeted by the major operators in the United States. 5G speeds depend on the distance from the tower and it greatly reduces after 1km.

5G Speeds Based on Distance Away From Site
PCMag has another interesting scenario about 5G speeds when it conducted a live testing at Michigan Avenue in Chicago.
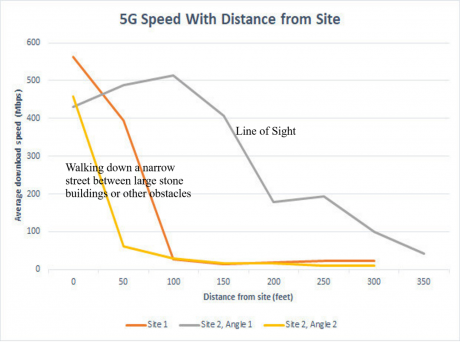
5G Speed With Distance From Site (Source: PCMag.com)
As shown above, the average download speed deteriorates to less than 50 Mbps when the distance from the site exceeds 50 to 100 feet (15m to 30m). This goes to show that multiple, low-height towers would likely be a mandatory requirement of 5G.
5G Types and Their Adopters
The four major US operators – AT&T, Verizon, T-Mobile and Sprint – have their own plans on building 5G networks for their customer bases. Their strategies are based on their existing wireless spectrum holdings as well as their future plans on fibre deployment to the tower which is necessary for building the fastest 5G type.
The following is a summary of 5G types and their adopters:
- mmWave high-band 5G: T-Mobile, AT&T and Verizon.
The high-band is about 10x faster than 4G LTE with extremely low latency, allowing individual messages to be transmitted almost instantaneously. However, the speed deteriorates rapidly as distance from the tower increases.
- Mid-band 5G: T-Mobile.
The mid-band is about 6x faster than 4G LTE. However, it has a smaller footprint than low-band.
- Low-band 5G: T-Mobile and AT&T.
The low-band is about 20 percent faster than 4G LTE.
These bands can also be illustrated in the following figure:
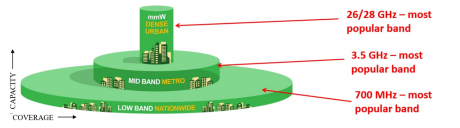
Typical 5G Frequency Bands (Source: Operator Watch Blog)
As shown above, the mmWave high-band which offers the highest capacity but lowest coverage is the most suitable for dense urban environments. The low-band which offers the widest coverage but lowest capacity is most suitable for rural coverage. The mid-band is in between the high-band and low-band in terms of capacity and coverage, and is suitable for metro environments.
Advantages of mmWave High-Band 5G
In a 4G network, a 4GB file download typically takes over 5 minutes (with a 100 Mbps connection). On a 5G network of mmWave high-band type, the same file would only take 32 seconds (with a 1Gbps connection). However, according to PCMag, this speed can only be achieved if the distance from the tower is less than 80 feet (25m).
Another advantage of the mmWave high-band 5G is its extremely low latency. This feature is especially useful in self-driving cars and online gaming, where spontaneous response is mandatory.
However, the mmWave high-band 5G is being rolled out by operators in very limited areas such as stadiums, arenas and other highly dense areas. Most of the other rollouts will be of mid-band or low-band type, which provide reasonable coverage but not extremely fast speeds.
Key Takeaways
- As with most of the new technologies, there is a lot of hype surrounding 5G speeds. Although lightning speed is achievable, most of the users will get only a fraction of it as they move away from the tower.
- The three major cellular operators in the US have different plans regarding the deployment of 5G networks. However, some applications do not require long-distance communication.
- For example, for communication among the “connected cars”, the required reach is within a few meters. Perhaps more of such applications will be developed in the next few years. Necessity is the mother of invention.
Follow us on LinkedIn to stay tuned to our weekly updates of the latest developments in the Telecom/IT industry and popular courses that we offer.
Share this on…
-
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in 5G Network Automations
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in 5G Network Automations
March 8, 2021 Category: 5G Technologies
5G networks and services will be empowered by network automation and big data – two major areas related to Artificial Intelligence (AI). More than half of service providers (53%) have already charted out plans to fully integrate some aspect of AI into their networks last year, with 19% estimating complete roll out within a period of 3 to 5 years.
Network Automation
Network automation is the process of automating the configuring, managing, testing, deploying, and operating of physical and virtual devices within a network.
Big Data
The term “Big Data” refers to large data sets that are analyzed to extract insights that enhance decision making. The process of automation takes place when device procedures are executed as per pre-programmed instructions.
5G can be intelligently harnessed to generate huge amounts of data in a distributed and decentralized system. This Big Data can be used for multiple objectives in several layers of the 5G architecture, through both local and centralized manners as shown below.
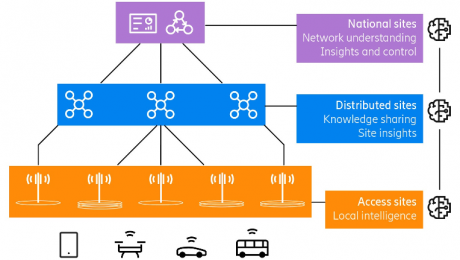
Learning and decision making in large distributed networks (Source: Ericsson)
However, as the deployment of new services such as SD-WAN and NFV further enhance the complexity of 5G networks, service providers would need to enhance the astuteness of their planning, deployment and operations, to meet the ever-increasing customer demands.
A 5-Step Model to Network Automation
Based on the “People, Process and Technology (PPT) framework”, a 5-step model has been proposed by some vendors to smoothen network automation. The five steps are as follows:

5-Step Model to Network Automation
It is important to note that the above processes may not always progress sequentially; there may be some overlaps and deviations on the vendors’ or customers’ end which may result in a hybrid model.
Based on the above, network automation and transition may follow a similar model with phases:
- Manual Operations: Traditional networks, requiring human intervention.
- Automated Workflows: Design, execution, and automation of processes
- Automation, Tests, and Networks, as code: Trigger actions automatically. Proactive instead of reactive troubleshooting
- Continuous Processes, Continuous Pipeline: Automate build, testing, deployment & response like engineering teams. Move quickly in small steps for agility with accuracy.
- Engineering Outcomes: Simplicity, Network Reliability, Business Agility, Continuous Improvement, Positive Outcomes
CSPs’ Next Move: Enhancing Customer Experience through AI
An increasing focus on customer experience (CX) improvement is actively shaping the business strategies of communications service providers (CSPs) globally.
With market disruptions, declines in traditional revenues, increasing competition and changing customers’ expectations, CSPs will need to strive to make CX a focal point of effort, investment and performance evaluation throughout their business value chains.
CSPs who are able to embrace Big Data developments and new disruptive technologies to provide users with seamless and personalised experiences across various touchpoints will be best poised for success.
To sum up, AI will complement 5G by enhancing the performance and robustness of networks, while 5G networks will continue to accelerate AI use cases. ABI Research estimates that this technical duo will increase global productivity across adjacent industries by 5.8% in 2035, which is equivalent to US$11.4 trillion in 2035.
Follow us on LinkedIn to stay tuned to our weekly updates of the latest developments in the Telecom/IT industry and popular courses that we offer.
Share this on…
-
SDN Architecture Explained: 5 Key Features
SDN Architecture Explained: 5 Key Features
January 15, 2021 Category: SDN NFV
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) is an architecture that aims to improve network control such that enterprises and service providers are able to respond swiftly to changing business requirements.
In a software-defined network, there is a physical separation between the network control plane and the user plane. The three main layers of the SDN architecture consists of the application layer, the control layer and the infrastructure layer.
The network control is empowered as directly programmable which enables the decoupling of the network control and forwarding functions. The core infrastructure is virtualized for applications and network services.
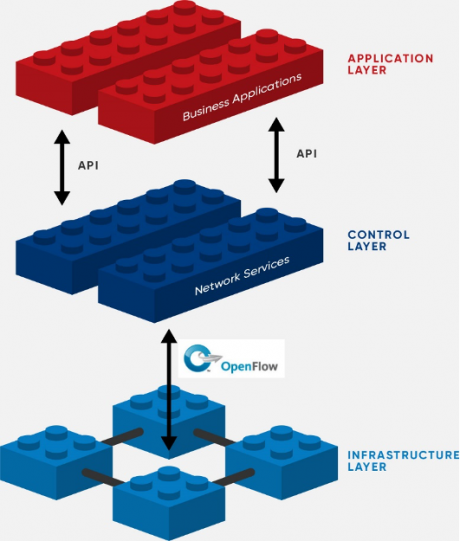
SDN Architecture (Source: ONF)
SDN architecture is:
DIRECTLY PROGRAMMABLE
Network control is made directly programmable by isolating it from forwarding functions. The core arrangement is virtualized for applications and network services.
AGILE
SDN requires swift tuning of network traffic flow to meet fluctuating traffic demand. This feature is called “agile” and is enabled by separating control from forwarding.
Agile principles and a DevOps approach are used to manage and curtail the network service deployment lifecycle.
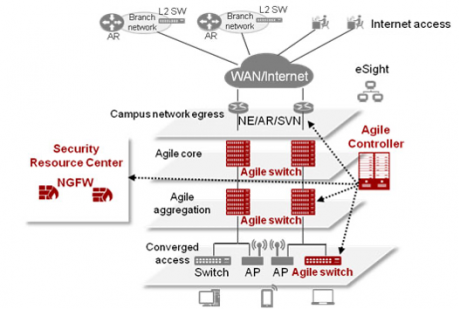
An Agile SDN adapting to rapid changes (Source: Huawei)
CENTRALLY MANAGED
Software-based SDN controllers contain network intelligence and keep a holistic view of the network. The applications and policy engines perceive it as a sole, logical switch.
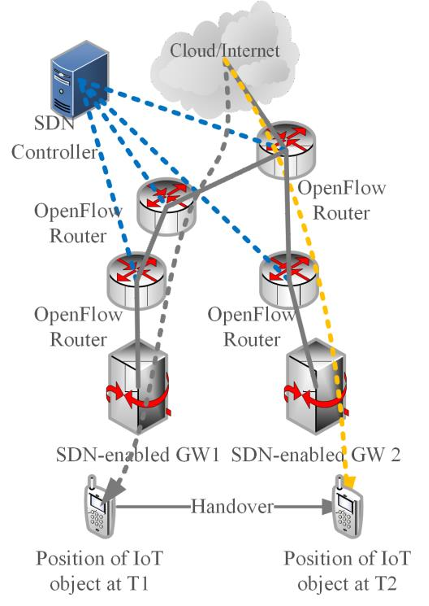
A centrally controlled SDN to improve mobility management (Source: Research Gate)
PROGRAMMATICALLY CONFIGURED
As explained earlier, SDN permits the abstraction of Control Plane from the Data Plane. This is made possible by using Application Programming Interfaces (API). This is in contrast to the legacy network functions, which were distinct hardware boxes, with a fixed set of features. With APIs and software upgrades, these features can be altered and new ones added by keeping the same hardware. It shortens the whole lifecycle from planning to installation and operations & maintenance. In addition, it results in a lot of savings in initial expenditure as well as we running expenses.
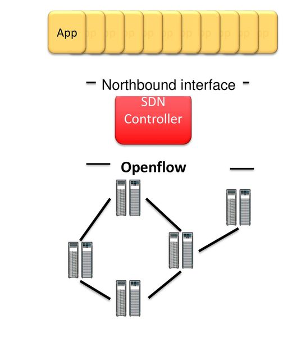
SDN Programming and APIs
OPEN STANDARDS-BASED AND VENDOR-NEUTRAL
To develop interfaces for software-defined networks, selected vendors have formed an industry group. It will integrate both the new OpenFlow methodology and legacy distributed networks. By using APIs, the trend is to move towards a vendor-neutral, hybrid approach that can incorporate currently distributed protocols as well as OpenFlow.
Multiple vendors interworking together
In conclusion, SDN architecture isolates the SDN control plane and the SDN data plane of the networking stack. Operators can benefit from the features such as programmable, swift, centrally managed and vendor-neutral & open standards. They do not need to replace their hardware after every few years, as by software patches, new features can be added. Shortly, we will see many transitions from hardware-based solutions to software-based services.
Telefocal Asia is a vendor-neutral training provider that specialises in SDN, NFV, SD-WAN training courses. We are an accredited training provider that helps prepare candidates for the MEF-certification exams via the MEF-CECP and MEF-SDCP courses. For more information on our training topics and content, please visit our website at www.telefocal.com.
Follow us on LinkedIn to stay tuned to our weekly updates of the latest developments in the Telecom/IT industry and popular courses that we offer.
Share this on…